Discovering Your Dog's Age in Human Years
Discovering Your Dog's Age in Human Years
Blog Article
Knowledge your dog's age in human decades is more than just a passing curiosity. It offers information in to your pet's life period, supporting you cater with their health, diet, and activity needs more effectively. But as the widely-known Dog age calculator system is common, it does not entirely reveal reality.
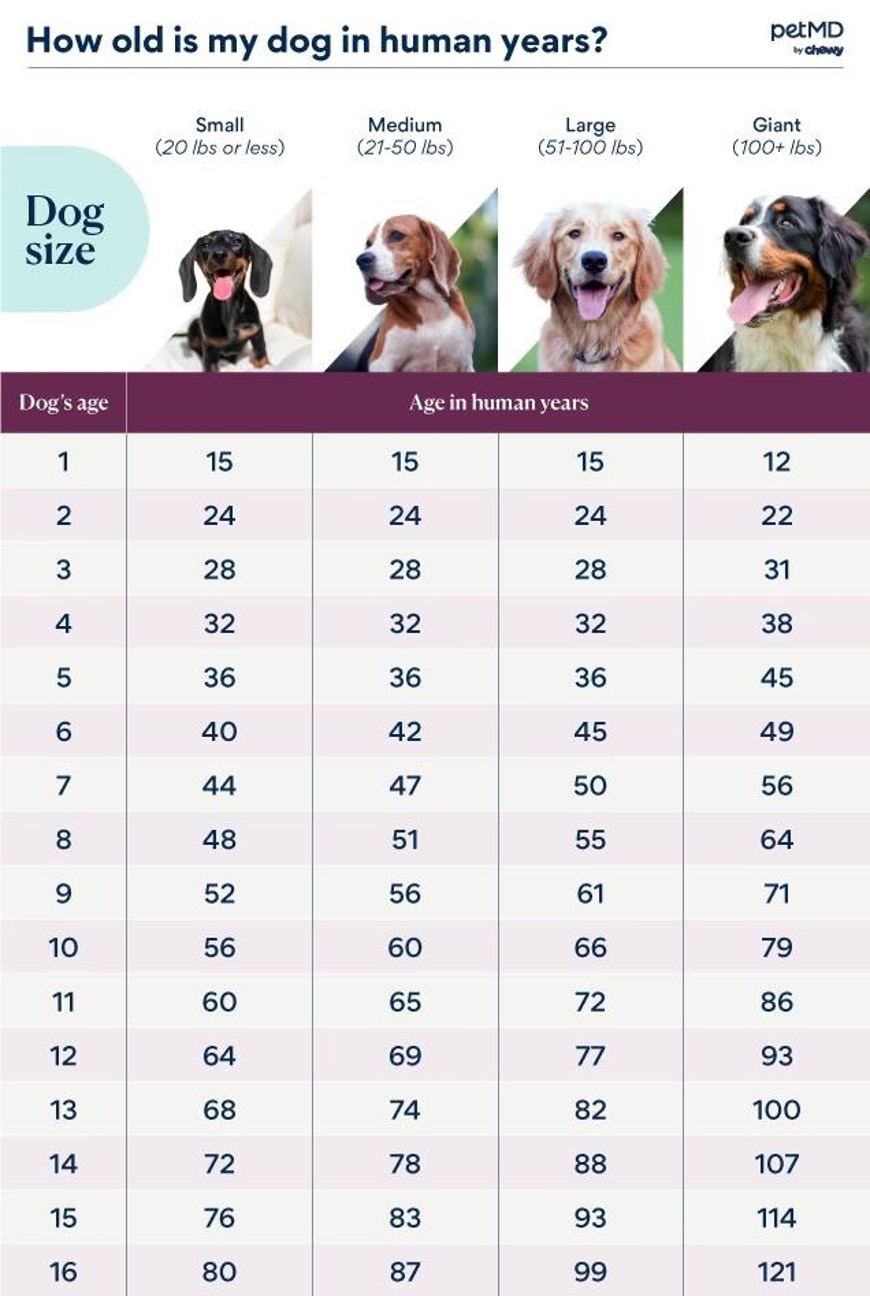
The Science Behind Pet Decades
The 7-to-1 principle oversimplifies how pets age. The velocity of aging differs depending on a dog's size, type, and their early development. Smaller breeds have a tendency to age slower and stay longer, while larger breeds era easily and normally have faster lifespans.
Researchers at the College of Florida developed a study centered on a dog's epigenetic clock (how DNA changes over time) to measure ageing more accurately. Relating to their results, a 1-year-old dog is around equivalent to a 30-year-old human due to quick growth in the early years. By the full time canine is 2 years of age, their human age is approximately 42. Following this period, the ageing method decreases significantly.
A Breed-Specific Dysfunction
Here is a standard perspective on aging across breeds:
Small Breeds (e.g., Dachshunds, Chihuahuas)
These dogs era slowly, and by their first year, they may be akin to a 15-year-old human. By the next year, they're about 24 in individual years. Each subsequent year provides 4-5 individual years.
Medium Breeds (e.g., Bulldogs, Beagles)
Medium-sized pets follow a slightly faster trajectory than smaller dogs. By era 2, they might be about 28 individual years of age, with each following year equating to 5-6 individual years.
Large Breeds (e.g., Labrador Retrievers, Shepherds)
Greater breeds show obvious accelerated aging. A 1-year-old big dog's development correlates to a 15-year-old human, advancing to 49 human decades by age 5.
Tailoring Care to Their "Individual Age"
By calculating your dog's human-equivalent era, you'll gain a clearer comprehension of how to manage their living stage. For instance:
Puppies (human baby equivalent): Give attention to training and socialization.
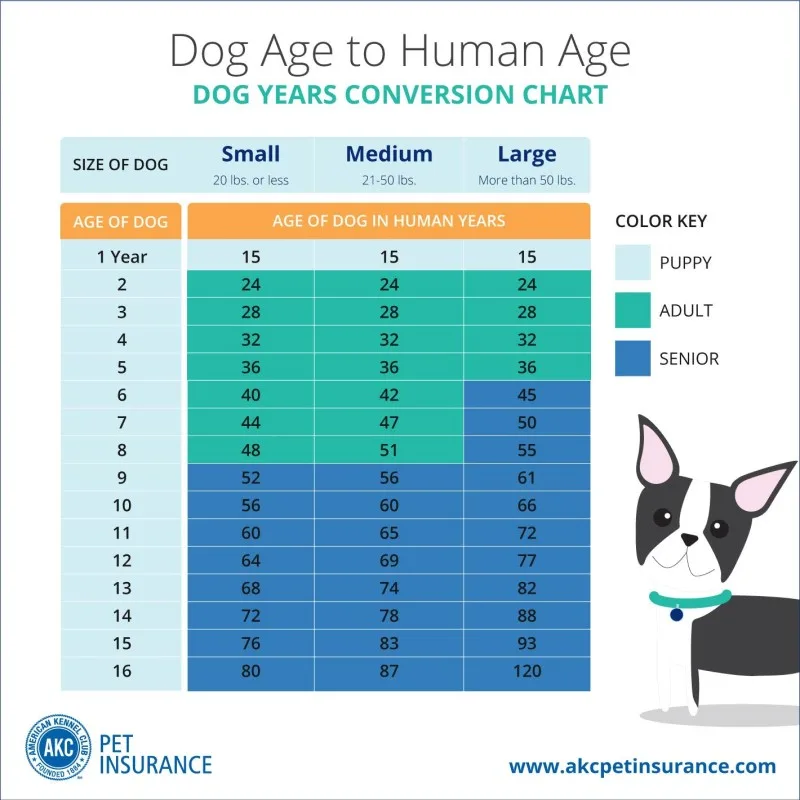
Adult dogs (human late 20s to 50s equivalent): Maintain their energy with a healthy diet and normal exercise.
Elderly dogs (human 60+ equivalent): Pay unique focus on mutual wellness, standard veterinarian visits, and smoother diets.
The link of pet years to individual decades allows pet owners the data they have to ensure their fuzzy buddies stay the happiest and healthiest lives possible.
Report this page